When capturing 802.15.4 related data from Sub 1 GHz networks, suitable front-end/s should be connected to the Perytons™ Protocol Analyzers.
There are 11 channels defined in the
Sub 1 GHz band (1 channel in 868.3 MHz and 10 channels within the 902 – 928 MHz
band).
Unlike the 2.4GHz band, the IEEE802.15.4 in the Sub 1 GHz bands allows
different modulation types and data rates (supported by some of the Sub 1 Ghz
front-ends) which are divided within pages, so the UI in the different relevant
sections of the Perytons™ Protocol Analyzers may look different.
This paragraph shows the capture forms used when capturing Sub 1 GHz network data.
Before a data capture of a Sub 1 GHz network takes place, the user needs to choose a Sub 1 GHz dongle option from the Dongle Type selection drop-down list in the Capture Form.
Similar to what is done when capturing 2.4GHz data, the user can choose the required channel manually or let the analyzer to automatically scan the channels for existing activity through the Passive Scan process (see chapter IV.11 for details on capturing data from 2.4GHz networks).
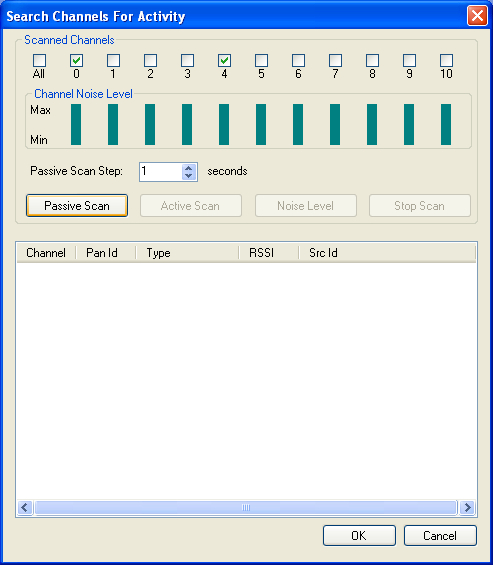
Search Channels For Activity - This form allows analyzing the existing ‘traffic picture'.

Figure 412 – Search Channels For Activity in SubGHz networks form
The 'Passive Scan' process searches for 802.15.4 based activity (e.g. ZigBee, 6LoWPAN). A list of devices found is displayed in a list format enabling the user to choose the relevant PAN, specific device (e.g. known coordinator) or just any channel where the RF activity of interest is present.
Note: Scan is performed for the current channel page selected and will not detect activity made in other modulations.
Data Capture 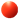
Figure 413 – Data Capture in SubGHz networks form
The user should choose what channel/s the analyzer should capture, a Sub 1 GHz dongle/s from the Dongle Type drop-down list and the requested page form the 'Page' drop-down list:
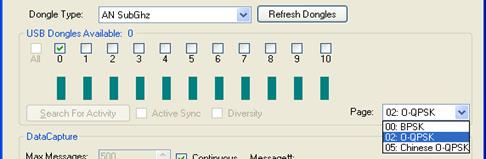
Figure 414 – SubGHz Page drop-down list
Similar to capturing data from 2.4GHz networks, a data capture process will start when pressing the "Start…" button (see chapter IV.11 for details about the different Data Capture Modes).